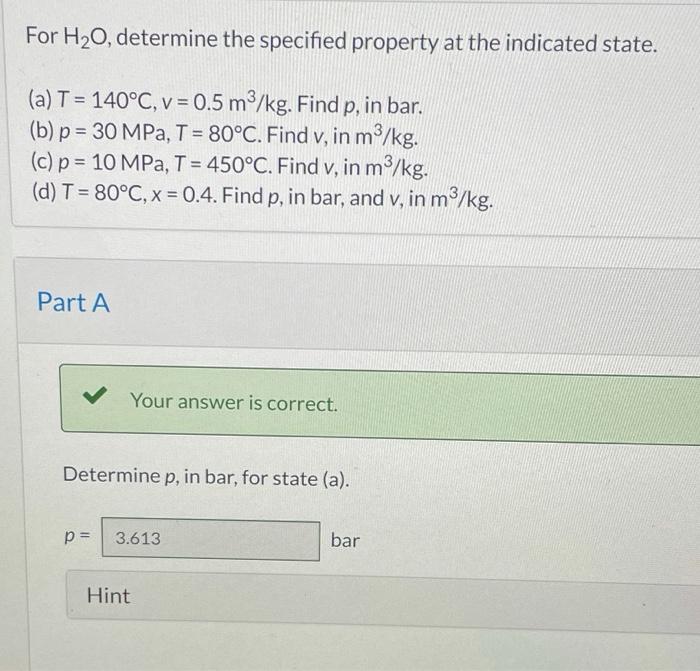
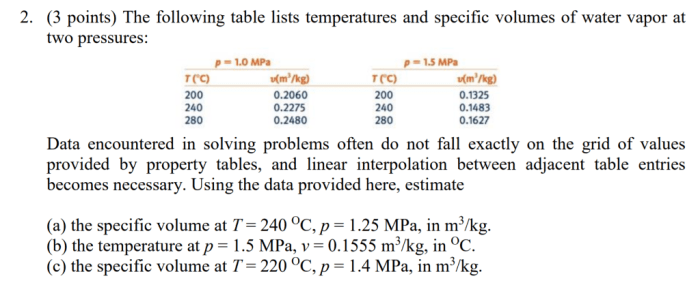
For h2o determine the specified property at the indicated state is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, providing a crucial understanding of the behavior and characteristics of water under various conditions. This exploration delves into the intricacies of thermodynamic properties, state variables, and specified properties, unveiling their significance in characterizing the state of a system and enabling accurate engineering applications.
Comprehending the specified properties of H2O empowers engineers and scientists to optimize processes, design systems, and predict the behavior of water in diverse applications, ranging from power generation to refrigeration and beyond.
Thermodynamic Properties

Thermodynamic properties are physical quantities that describe the state of a system. They can be used to predict the behavior of a system and to design and optimize processes.
Thermodynamic properties can be classified into two types: extensive and intensive. Extensive properties are those that depend on the amount of matter in the system, such as mass, volume, and energy. Intensive properties are those that do not depend on the amount of matter in the system, such as temperature, pressure, and density.
Some common thermodynamic properties include:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Volume
- Mass
- Energy
- Enthalpy
- Entropy
- Specific heat
State of a System
The state of a system is a complete description of its physical properties. The state of a system can be represented by a set of state variables, such as pressure, temperature, and volume.
The state of a system can be represented on a phase diagram. A phase diagram is a graph that shows the different phases of a substance as a function of temperature and pressure.
Specified Properties
Specified properties are thermodynamic properties that are used to characterize the state of a system. Some common specified properties include:
- Enthalpy
- Entropy
- Specific heat
Specified properties can be used to predict the behavior of a system and to design and optimize processes.
H2O
H2O is a common substance that exists in all three phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
The properties of H2O change with temperature and pressure. For example, the density of water decreases as the temperature increases.
Determining Specified Properties
There are a number of different methods for determining specified properties. These methods include:
- Using property tables and charts
- Using equations of state
- Using experimental data
The choice of method depends on the accuracy required and the availability of data.
Applications, For h2o determine the specified property at the indicated state
Specified properties are used in a wide variety of engineering applications. Some common applications include:
- Designing and optimizing heat exchangers
- Calculating the efficiency of power plants
- Predicting the behavior of fluids in pipelines
Accurate property data is essential for the design and optimization of engineering processes.
FAQ Resource: For H2o Determine The Specified Property At The Indicated State
What are specified properties?
Specified properties are intensive properties that characterize the state of a system, such as enthalpy, entropy, and specific heat, providing insights into the energy and disorder of the system.
How are specified properties used in engineering applications?
Specified properties are essential for designing and optimizing engineering systems, enabling engineers to predict the behavior of fluids, design heat exchangers, and analyze thermodynamic processes.
What are the different methods for determining specified properties?
Specified properties can be determined using property tables and charts, equations of state, and experimental measurements, providing accurate data for engineering calculations.