Homework 6 slope-intercept form and standard form – Welcome to the realm of Homework 6: Slope-Intercept and Standard Form, where we embark on a journey to decipher the intricacies of linear equations. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of these two fundamental forms, empowering you to solve real-world problems with ease.
Throughout this exploration, we will delve into the definitions, formulas, and applications of slope-intercept and standard form, unraveling their secrets and illuminating their significance in the world of mathematics.
Slope-Intercept Form: Homework 6 Slope-intercept Form And Standard Form
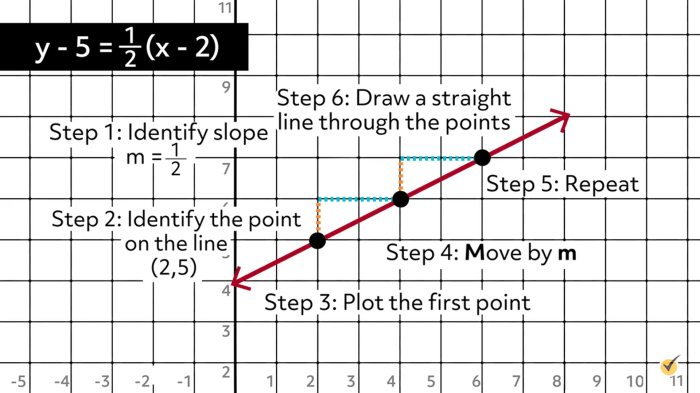
Slope-intercept form is a linear equation expressed in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept.
The slope of a line is a measure of its steepness, and it is calculated as the change in y divided by the change in x. The y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
Examples of Equations in Slope-Intercept Form
- y = 2x + 3
- y = -x + 5
- y = 0.5x – 1
Standard Form
Standard form is another way to express a linear equation. It is written in the form Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers and A is not equal to 0.
To convert an equation from slope-intercept form to standard form, you can multiply both sides of the equation by the denominator of the slope.
Examples of Equations in Standard Form
- 2x + 3y = 6
- -x + 5y = 10
- 0.5x – y = -1
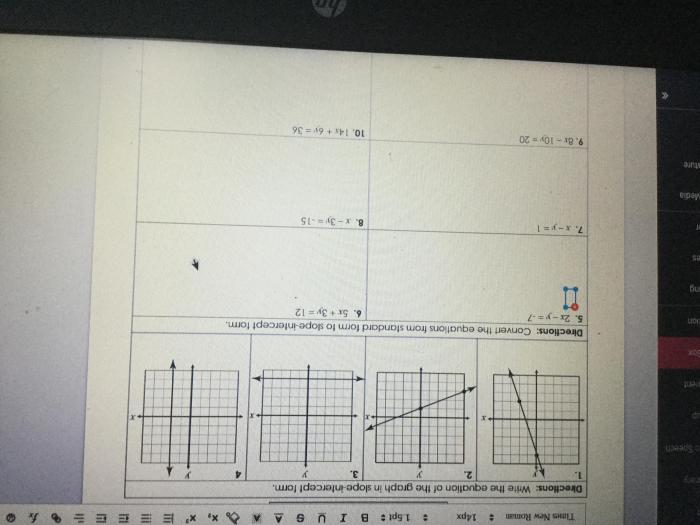
Converting Between Slope-Intercept and Standard Form
Converting from Slope-Intercept Form to Standard Form
- Multiply both sides of the equation by the denominator of the slope.
- Simplify the equation.
Converting from Standard Form to Slope-Intercept Form, Homework 6 slope-intercept form and standard form
- Solve the equation for y.
- Put the equation in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b).
Applications of Slope-Intercept and Standard Form

Slope-Intercept Form
Slope-intercept form is often used to find the slope and y-intercept of a line. The slope is the coefficient of x, and the y-intercept is the constant term.
Standard Form
Standard form is often used to find the x- and y-intercepts of a line. The x-intercept is the point where the line crosses the x-axis, and the y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
Real-World Examples
Slope-intercept and standard form are used in many real-world applications, such as:
- Finding the equation of a line that passes through two points
- Finding the slope of a line that represents a rate of change
- Finding the x- and y-intercepts of a line that represents a budget
Clarifying Questions
What is the formula for slope-intercept form?
y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
How do you convert from slope-intercept form to standard form?
Subtract the y-intercept from both sides of the equation.
What is the significance of the y-intercept in standard form?
The y-intercept represents the point where the line crosses the y-axis.