Review sheet the axial skeleton exercise 9 – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of the axial skeleton through Review Sheet: The Axial Skeleton (Exercise 9). This engaging guide provides an in-depth understanding of the structure, function, and components of this vital anatomical framework.
Delve into the intricacies of the vertebral column, thoracic cage, and skull, gaining insights into their unique characteristics and roles within the axial skeleton.
Axial Skeleton Overview
The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the body and consists of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. It provides support, protection, and attachment for the muscles and organs.
The axial skeleton is located along the midline of the body and extends from the skull to the pelvis. It is composed of 80 bones, which are connected by joints and ligaments to form a rigid framework.
Diagram of the Axial Skeleton:[Gambar diagram axial skeleton di sini]
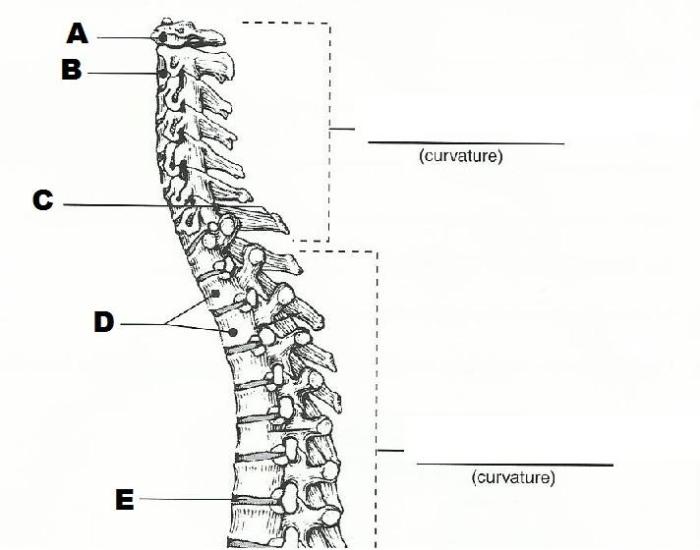
Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone, is a flexible, segmented structure that extends from the skull to the pelvis. It provides support, protection, and mobility for the spinal cord and other structures.
The vertebral column is divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal.
Regions of the Vertebral Column
| Region | Number of Vertebrae | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical | 7 | Small, flexible vertebrae with a foramen for the spinal cord |
| Thoracic | 12 | Larger vertebrae with ribs attached to form the thoracic cage |
| Lumbar | 5 | Large, strong vertebrae that support the weight of the upper body |
| Sacral | 5 (fused) | Fused vertebrae that form the sacrum, which supports the pelvis |
| Coccygeal | 4 (fused) | Small, fused vertebrae that form the tailbone |
Thoracic Cage: Review Sheet The Axial Skeleton Exercise 9
The thoracic cage is a protective structure that surrounds the heart, lungs, and other organs in the chest cavity. It is formed by the ribs, sternum, and thoracic vertebrae.
The ribs are curved bones that attach to the thoracic vertebrae. The sternum is a flat bone that forms the front of the thoracic cage. The thoracic cage provides protection and support for the internal organs and facilitates breathing.
Components of the Thoracic Cage
- 12 pairs of ribs
- Sternum
- 12 thoracic vertebrae
Illustration of the Thoracic Cage:[Gambar ilustrasi thoracic cage di sini]
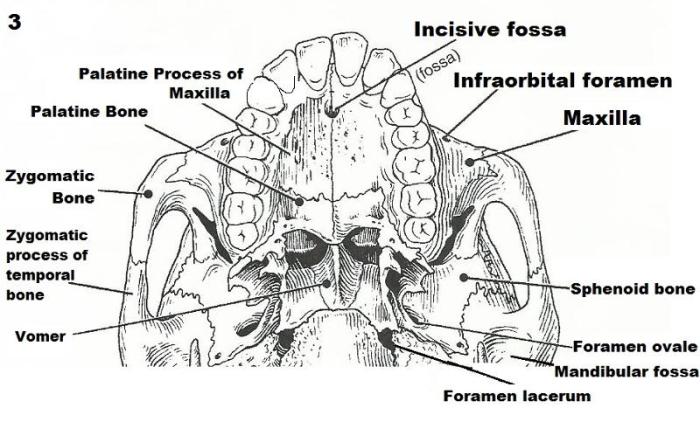
Skull
The skull is a complex structure that forms the head and protects the brain and other sensory organs. It is composed of 22 bones that are fused together to form a rigid framework.
The skull is divided into two main regions: the cranium and the facial skeleton.
Bones of the Skull, Review sheet the axial skeleton exercise 9
| Bone | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Forehead | Protects the brain |
| Parietal | Sides and top of the skull | Protects the brain |
| Occipital | Back of the skull | Protects the brain and forms the foramen magnum |
| Temporal | Sides of the skull | Protects the brain and contains the organs of hearing |
| Sphenoid | Base of the skull | Supports the brain and forms part of the eye sockets |
| Ethmoid | Base of the skull | Forms part of the eye sockets and nasal cavity |
| Nasal | Bridge of the nose | Supports the nose |
| Lacrimal | Medial wall of the eye socket | Forms part of the tear duct |
| Zygomatic | Cheekbone | Supports the cheek and forms part of the eye socket |
| Maxilla | Upper jaw | Supports the teeth and forms part of the nasal cavity |
| Mandible | Lower jaw | Supports the teeth and allows for chewing |
Axial Skeleton Muscles
The axial skeleton is associated with several muscles that facilitate movement and support the body. These muscles include:
- Trapezius:Extends from the base of the skull to the shoulder blades and assists in shrugging and rotating the shoulders.
- Sternocleidomastoid:Extends from the base of the skull to the sternum and clavicle and assists in turning and flexing the head.
- Scalenes:Located on the sides of the neck and assist in bending and rotating the neck.
- Erector spinae:A group of muscles that run along the back and assist in extending the spine.
- Rectus abdominis:A muscle located on the front of the abdomen and assists in flexing the spine and pelvis.
Diagram of Axial Skeleton Muscles:[Gambar diagram axial skeleton muscles di sini]
FAQ Insights
What is the primary function of the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton provides structural support, protects vital organs, facilitates movement, and houses the central nervous system.
How many vertebrae are there in the human vertebral column?
There are 33 vertebrae in the human vertebral column, divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal.
What is the role of the ribs in the thoracic cage?
The ribs form the protective framework of the thoracic cage, providing support for the lungs, heart, and other thoracic organs.